Ear Problems and Injuries, Age 11 and Younger
Overview
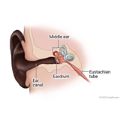
Ear pain in children may be a sign of an infection in the space behind the eardrum (middle ear). Ear infections (otitis media) most often occur when children have cold symptoms, such as a runny or stuffy nose and a cough, for a few days.
An ear infection may occur when the eustachian tube swells and closes and fluid builds up in the middle ear. The combination of fluid and germs (from bacteria or viruses) creates a perfect environment for an infection. Swelling from the infection can cause pain from increased pressure on the eardrum. The pressure can cause the eardrum to rupture (perforate). A single eardrum rupture is not serious and does not cause hearing loss. Repeated ruptures may lead to hearing loss.
Middle ear infections happen more often in children than in adults. Young children have short, soft, more horizontal eustachian tubes that are more easily blocked than those of older children and adults.
Ear infection is the most commonly diagnosed bacterial infection in young children. Almost all children will have at least one ear infection by the time they are school age. Most ear infections occur in babies between the ages of 6 months to 2 years. As children get older, ear problems may be related to inflammation, infection, or fluid buildup in the middle or external ear. Ear infections most often occur in children who:
- Spend time in day care settings.
- Use a pacifier.
- Aren't breastfed.
- Live in households where parents or caregivers smoke.
- Have had a previous ear infection.
- Have had certain conditions since birth. These may include cleft lip, cleft palate, or Down syndrome.
- Have allergies.
Fluid often remains in the middle ear (serous otitis, or middle ear effusion) after an ear infection. This may cause no symptoms, or it may cause a muffling of sound, decreased hearing, and mild discomfort. The body usually reabsorbs fluid behind the eardrum within 3 months, and hearing returns to normal. Some children have ear infections that keep coming back or fluid in the middle ear that doesn't go away.
Even though ear infections are a common cause of ear pain, not all ear pain means an infection. Other common causes of what seems like ear pain in young children include:
- Teething.
- A sore throat.
- A build-up of earwax.
- An object in the ear.
- Air pressure changes, such as when flying in an airplane.
- Fluid buildup without infection (serous otitis).
When checking ear pain in a child, remember that ear infections most often occur after a child has had cold symptoms for a few days. When a child has other symptoms, such as a fever, then the ear pain or drainage may be less important than the other symptoms.
Ear problems caused by an injury to the ear can occur at any age. Here are some common injuries:
- A fall or a forceful, direct blow to the side of the head can burst the eardrum or damage the tiny bones in the inner ear that send sound to the brain.
- An injury during contact sports can cause an injury, such as "cauliflower" ear from wrestling.
- Loud noises or explosions can damage the eardrum (acoustic trauma).
- Atmospheric pressure changes (barotrauma) can cause problems with the eustachian tube and trap air in or keep air out of the middle ear. Middle ear problems can be severe. For example, the eardrum can burst or the middle ear can fill with blood or pus. Or they can be mild and only be felt as changes in pressure.
- Cuts or scrapes may injure the outside of the ear or ear canal.
- Cleaning the ear canal too often, too forcefully, or with a cotton swab, bobby pin, or sharp fingernail can cause irritation or injury.
- Burns or frostbite can cause ear injuries (thermal injuries).
- Objects placed in the ear can cause injury to the ear canal or the eardrum (tympanic membrane).
Check Your Symptoms
The medical assessment of symptoms is based on the body parts you have.
- If you are transgender or nonbinary, choose the sex that matches the body parts (such as ovaries, testes, prostate, breasts, penis, or vagina) you now have in the area where you are having symptoms.
- If your symptoms aren’t related to those organs, you can choose the gender you identify with.
- If you have some organs of both sexes, you may need to go through this triage tool twice (once as "male" and once as "female"). This will make sure that the tool asks the right questions for you.
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), medicines that suppress the immune system like steroids or chemotherapy, herbal remedies, or supplements can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
Temperature varies a little depending on how you measure it. For children up to 11 years old, here are the ranges for high, moderate, and mild according to how you took the temperature.
Oral (by mouth), ear, or rectal temperature
- High: 104° F (40° C) and higher
- Moderate: 100.4° F (38° C) to 103.9° F (39.9° C)
- Mild: 100.3° F (37.9° C) and lower
A forehead (temporal) scanner is usually 0.5° F (0.3° C) to 1° F (0.6° C) lower than an oral temperature.
Armpit (axillary) temperature
- High: 103° F (39.5° C) and higher
- Moderate: 99.4° F (37.4° C) to 102.9° F (39.4° C)
- Mild: 99.3° F (37.3° C) and lower
Note: For children under 5 years old, rectal temperatures are the most accurate.
A baby that is extremely sick:
- May be limp and floppy like a rag doll.
- May not respond at all to being held, touched, or talked to.
- May be hard to wake up.
A baby that is sick (but not extremely sick):
- May be sleepier than usual.
- May not eat or drink as much as usual.
If you're not sure if a child's fever is high, moderate, or mild, think about these issues:
With a high fever:
- The child feels very hot.
- It is likely one of the highest fevers the child has ever had.
With a moderate fever:
- The child feels warm or hot.
- You are sure the child has a fever.
With a mild fever:
- The child may feel a little warm.
- You think the child might have a fever, but you're not sure.
Certain health conditions and medicines weaken the immune system's ability to fight off infection and illness. Some examples in children are:
- Diseases such as diabetes, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and congenital heart disease.
- Steroid medicines, which are used to treat a variety of conditions.
- Medicines taken after organ transplant.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer.
- Not having a spleen.
Symptoms of an external ear infection may include:
- Moderate to severe pain in the outer ear.
- Pain with chewing.
- Redness and swelling of the ear, ear canal, or the skin around or behind the ear.
Vertigo is the feeling that you or your surroundings are moving when there is no actual movement. It may feel like spinning, whirling, or tilting. Vertigo may make you sick to your stomach, and you may have trouble standing, walking, or keeping your balance.
Pain in children under 3 years
It can be hard to tell how much pain a baby or toddler is in.
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the baby cannot sleep, cannot get comfortable, and cries constantly no matter what you do. The baby may kick, make fists, or grimace.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The baby is very fussy, clings to you a lot, and may have trouble sleeping but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The baby is a little fussy and clings to you a little but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
Pain in children 3 years and older
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the child can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain. No one can tolerate severe pain for more than a few hours.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt the child's normal activities and sleep, but the child can tolerate it for hours or days.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The child notices and may complain of the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt his or her sleep or activities.
Seek Care Today
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor or telehealth provider today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or telehealth provider or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Make an Appointment
Based on your answers, the problem may not improve without medical care.
- Make an appointment to see your doctor in the next 1 to 2 weeks, or contact your telehealth provider.
- If appropriate, try home treatment while you are waiting for the appointment.
- If symptoms get worse or you have any concerns, call your doctor or telehealth provider. You may need care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Self-Care
When ear discomfort or pain is mild or it comes and goes and occurs without other symptoms, home treatment may be all that is needed. Here are some things you can do to help your child feel better.
- Encourage your child to swallow more often. The discomfort may be caused by a blocked eustachian tube that can occur with mild irritation in the ear canal. If your child is younger than age 12 months, let your child drink from a bottle or cup to try to help open the eustachian tube.
- Some babies and children who have mild ear pain are more comfortable in an upright position. Allow your child to rest in the position that is most comfortable.
- To relieve a red, swollen external ear:
- Put ice or a cold pack on the ear for 10 to 20 minutes at a time. Put a thin cloth between the ice and your child's skin.
- Encourage your child to rest as much as possible.
When to call for help during self-care
Call a doctor if any of the following occur during self-care at home:
- New or worse pain.
- New or worse signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, swelling, or a fever.
- New or worse drainage from the ear.
- New symptoms develop, such as hearing loss or dizziness.
- Symptoms occur more often or are more severe.
Learn more
Over-the-counter medicines
- Acetaminophen
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Quick Tips: Safely Giving Over-the-Counter Medicines to Children
More self-care
Watch
Preparing For Your Appointment
You can help your doctor diagnose and treat your condition by being prepared for your appointment.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: October 27, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: October 27, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.