Ulcerative Colitis
Condition Basics
What is ulcerative colitis?
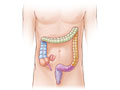
Ulcerative colitis is a disease that causes inflammation and sores (ulcers) in the lining of the large intestine, or colon, Opens dialog. It usually affects the lower section and the rectum. But it can affect the entire colon. In general, the more of the colon that's affected, the worse the symptoms will be.
What causes it?
Experts aren't sure what causes ulcerative colitis. It might be caused by the immune system overreacting to normal bacteria in the digestive tract. Or other kinds of bacteria and viruses may cause it. You are more likely to get it if other people in your family have it.
What are the symptoms?
The main symptoms of ulcerative colitis are belly pain or cramps, diarrhea, and bleeding from the rectum. In severe cases, people may have diarrhea 10 to 20 times a day. Some people also may have a fever, not feel hungry, and lose weight. In most people, the symptoms come and go.
How is it diagnosed?
To diagnose ulcerative colitis, a doctor will ask about your symptoms, do a physical exam, and do a number of tests. These tests may include colonoscopy, blood tests, and stool sample testing. Testing can help rule out other problems that can cause similar symptoms, such as Crohn's disease and irritable bowel syndrome.
How is ulcerative colitis treated?
Medicines can help reduce your symptoms and help you avoid new flare-ups. If you have severe symptoms and medicines don't help, you may need surgery to remove your colon. This cures ulcerative colitis.
Health Tools
Health Tools help you make wise health decisions or take action to improve your health.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of ulcerative colitis are:
- Belly pain or cramps.
- Diarrhea.
- Bleeding from the rectum.
Some people also may have a fever, may not feel hungry, and may lose weight. In severe cases, people may have diarrhea 10 to 20 times a day.
The disease can also cause other problems, such as joint pain, eye problems, skin problems, or liver disease.
In most people, the symptoms come and go. Some people go for months or years without symptoms (remission) and then have a flare-up. A few people have symptoms all the time.
What Happens
Ulcerative colitis may be mild, moderate, or severe.
Most people have periods of remission (when the condition is not active) that may last months or years. During these periods, people may sometimes have flare-ups with moderate symptoms. Some people have symptoms all the time.
Children may have the same symptoms that adults have. Also, children with the disease may grow more slowly than normal and go through puberty later than expected.
Complications of ulcerative colitis
Problems from ulcerative colitis can include:
- Narrowed areas of the intestine (strictures). They can make it hard to pass stools.
- Increased risk of cancer of the colon and rectum. Your risk may start to go up after 8 to 10 years. Your risk is highest if a lot of your colon is involved.
- Problems outside the digestive tract. These include joint pain, skin problems, eye problems, or liver disease.
- The colon swelling to many times its normal size. This is called toxic megacolon, Opens dialog. It's rare, but it needs treatment right away.
- Other rare problems, such as scarring of the bile ducts and the pancreas, Opens dialog.
- Increased risk of melanoma, a serious type of skin cancer. Your doctor may recommend regular screening by a dermatologist.footnote 1
Irritable bowel syndrome
Some people who have ulcerative colitis also have irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Opens dialog. It isn't as serious as ulcerative colitis. IBS causes belly pain along with diarrhea or constipation.
Learn more
When to Call
Ulcerative Colitis: When to Call
Call 911 anytime you think you may need emergency care. For example, call if:
- You passed out (lost consciousness).
- Your stools are maroon or very bloody.
- You have severe belly pain with or without bloating.
Call a doctor now if you have been diagnosed with ulcerative colitis and you have:
- New or worse belly pain.
- Fever or shaking chills.
- Severe dehydration, Opens dialog.
- New or worse nausea or vomiting.
- New or more blood in your stools.
- Problems passing any stools or gas.
- Pus draining from the area around the anus, Opens dialog, or pain and swelling in the anal area.
If you have any of these symptoms and you have been diagnosed with ulcerative colitis, your disease may have become much worse. Some of these symptoms, such as severe belly pain and bloating, also may be signs of toxic megacolon, Opens dialog. This is a condition in which the colon swells to many times its normal size. It requires emergency treatment. Without treatment, it can cause the colon to leak or rupture, which can be fatal.
People with ulcerative colitis usually know their normal pattern of symptoms. Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if:
- You have new or worse symptoms, such as diarrhea that gets worse or lasts for more than 2 weeks.
- You are losing weight.
- You do not get better as expected.
Watchful waiting
Watchful waiting is not a good choice when you have any of the above symptoms. If your symptoms are caused by ulcerative colitis, delaying the diagnosis and treatment may make the disease worse. And it can increase your risk of other problems.
Even when the disease is in remission, your doctor will want to see you regularly to check for complications. Some of these problems can be hard to detect. It's always a good idea to call your doctor's office for advice.
Check your symptoms
Exams and Tests
To diagnose ulcerative colitis, a doctor will ask about your symptoms, do a physical exam, and do a number of tests. Testing can help rule out other problems that can cause similar symptoms, such as Crohn's disease and irritable bowel syndrome.
Tests that may be done include:
- Colonoscopy. In this test, a doctor uses a thin, lighted tool to look at the inside of your entire colon. At the same time, the doctor may take a sample (biopsy) of the lining of the colon.
- Blood tests to check for infection or inflammation.
- Stool sample testing to look for blood, infection, and white blood cells.
Learn more
Watch
Treatment Overview
Treatment is done to improve your symptoms and to heal your colon. Treatment depends on:
- How bad the disease is.
- What treatments have worked.
- Your age.
- If you have certain infections, such as Clostridioides difficile (or C. diff).
Medicines.
- For mild or moderate cases of the disease when there is little risk of needing surgery, most people can be treated with pills or rectal medicines. These medicines reduce inflammation and calm down the immune system. Some people need steroid medicines.
- For moderate or severe cases of the disease when there is a high risk of needing surgery, medicines (such as biologics) are used to prevent inflammation. These are given intravenously (I.V.) or as a shot. Other medicines to calm down the immune system may be needed. Some people need steroid medicines.
Surgery.
You might need surgery to remove the colon:
- If it's an emergency, such as a problem like toxic megacolon.
- If medicines don't help your symptoms, or if side effects are causing problems.
Surgery almost completely reduces the risk of colon cancer.
Learn more
Self-Care
You can take steps at home to reduce symptoms of ulcerative colitis and take care of yourself.
- Take diarrhea medicines.
If your diarrhea isn't well controlled, ask your doctor if there are over-the-counter medicines you can use.
- Avoid medicines that can make ulcerative colitis worse.
In general, doctors recommend that you don't use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen). These medicines may cause flare-ups. But some people may be more likely to have flare-ups from NSAIDs than other people. Talk to your doctor about whether to avoid these medicines.
- Pay attention to what you eat and drink.
During a flare-up, avoid foods that make your symptoms worse. This may include foods that are high in fiber or high in fat. It may also include foods and drinks that have lactose, like dairy products.
Focus on getting enough fluids and on eating enough protein.
In between flares, you can go back to eating your normal diet.
- Get support.
Ulcerative colitis can affect every aspect of your life. You may want to seek counseling or social support from family, friends, or a faith leader. Or look for a support group.
Children can have worse ulcerative colitis symptoms than adults. It also can cause them to grow more slowly or even stop growing. That's why it's important to get care right away and follow a treatment plan. Support groups can provide emotional support as well as information to help a child cope with ulcerative colitis.
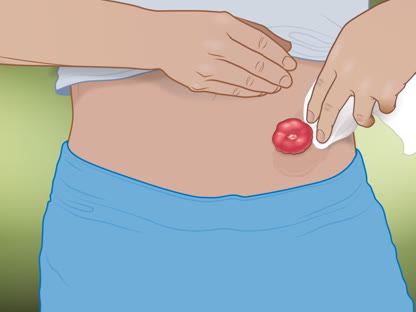
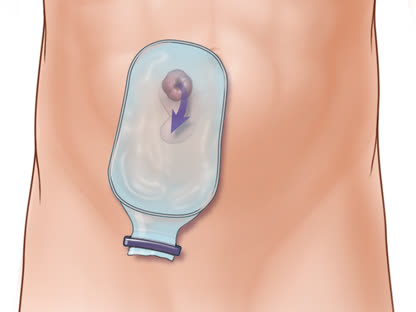
- Learn about ostomy care.
If you have had or are planning to have surgery that will create an ostomy, Opens dialog, you may feel self-conscious or embarrassed. After a period of adjustment, most people are able to resume all of their usual activities. In fact, you may feel better than before surgery because you may no longer have painful symptoms. Support groups are available for people with ostomies.
Learn more
Watch
Medicines
Medicines are the main treatment for ulcerative colitis. They are used to control inflammation in the intestines and then keep it from coming back. Your doctor will talk to you about your choices.
For mild or moderate cases of the disease when there is little risk of needing surgery, most people use aminosalicylates or steroid medicines. These can be taken as a pill, suppository, rectal foam, or enema.
For moderate or severe cases of the disease when there is a high risk of needing surgery, you will need medicines (such as biologics) to prevent inflammation. These are given intravenously (I.V.) or as a shot. Many people also need aminosalicylates, steroid medicines, or other medicines to calm down the immune system.
If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, talk to your doctor about which medicines are safest.
Surgery
Surgery that removes the large intestine (colon), Opens dialog can cure ulcerative colitis. It may help problems that the disease causes outside the colon, such as slowed growth in children.
People need surgery for different reasons. For example, it may be needed when treatment isn't working or when holes form in the large intestine.
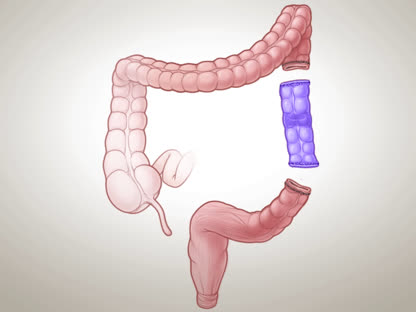
These are the two most common types of surgery.
- Ileoanal anastomosis.
-
The surgeon removes some or all of the large intestine, and the lining of the rectum. Then the surgeon connects the small intestine to the anal canal. After this surgery, you can have bowel movements without an ostomy, Opens dialog.
- Proctocolectomy and ileostomy.
-
The surgeon removes the large intestine and rectum. Then the surgeon sews the anus closed and creates an opening to the outside of the body. After this surgery, you'll need an ostomy.
Learn more
Watch
Related Information
References
Citations
Credits
Current as of: October 19, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: October 19, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.